


Next: 13.6 Phase Referencing
Up: 13 PHASE CALIBRATION &
Previous: 13.4 Editing
Contents
13.5 Self-Calibration, Imaging, & Deconvolution
Even after global fringe fitting, averaging, and editing, the
phases on a VLBA target source can still vary rapidly with time. Most
of these variations are due to inadequate removal of station-based
atmospheric phases, but some variations also can be caused by an
inadequate model of the source structure during fringe fitting. If
the VLBA target source is sufficiently strong and if absolute
positional information is not needed, then it is possible to reduce
these phase fluctuations by looping through cycles of Fourier transform
imaging and deconvolution, combined with phase self-calibration in a
time interval shorter than that used for the fringe fit (Cornwell
1995; Walker 1995b; Cornwell & Fomalont 1999). Fourier transform
imaging is straightforward (Briggs, Schwab, & Sramek 1999), and done
with AIPS task IMAGR or the Caltech program Difmap
(Shepherd 1997). The resulting VLBI images are deconvolved to rid
them of substantial sidelobes arising from relatively sparse sampling
of the 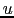 -
-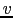 plane (Cornwell, Braun, & Briggs 1999). Such
deconvolution is achieved with AIPS tasks based on the CLEAN or
Maximum Entropy methods or with the Caltech program Difmap.
plane (Cornwell, Braun, & Briggs 1999). Such
deconvolution is achieved with AIPS tasks based on the CLEAN or
Maximum Entropy methods or with the Caltech program Difmap.
Phase self-calibration just involves minimizing the difference
between observed phases and model phases based on a trial image, by
solving for station-based instrumental phases (Cornwell 1995; Walker
1995b; Cornwell & Fomalont 1999). After removal of these
instrumental phases, the improved visibilities are used to generate
an improved set of model phases, usually based on a new deconvolved
trial image. This process is iterated several times until the phase
variations are substantially reduced. The method is then generalized
to allow estimation and removal of complex instrumental antenna gains,
leading to further image improvement. Both phase and complex
self-calibration can be accomplished using AIPS task CALIB or
with the Caltech program Difmap.
Self-calibration should only be done if the VLBA target source is
detected with sufficient signal-to-noise in the self-calibration time
interval (otherwise, fake sources can be generated!) and if absolute
positional information is not needed.
The useful field of view in VLBI images can be limited by finite
bandwidth, integration time, and non-coplanar baselines (Wrobel 1995;
Cotton 1999b; Bridle & Schwab 1999; Perley 1999b); the first two of
these effects are described in Section 7.3. Measures
of image correctness - image fidelity and dynamic range - are
discussed by Walker (1995a) and Perley (1999a).



Next: 13.6 Phase Referencing
Up: 13 PHASE CALIBRATION &
Previous: 13.4 Editing
Contents
Jon Romney
2012-01-05