


Next: 17.2 Submitting a Proposal
Up: 17 VLBA/HSA/EVN/GLOBAL PROPOSALS
Previous: 17 VLBA/HSA/EVN/GLOBAL PROPOSALS
Contents
17.1 Preparing a Proposal
Observing proposals may specify the VLBA, or the VLBA in combination with
various other VLBI arrays:
- The VLBA alone.
A Call for Proposals is published
in the NRAO eNews at http://science.nrao.edu/enews/ approximately
two weeks in advance of each trimester submission deadline. Currently,
these deadlines are February 1, June 1, and October 1. (Deadlines are
delayed until the following Monday if these dates fall on Saturday or Sunday.)
A description of time allocation may be found at
http://www.aoc.nrao.edu/epo/ad/scheduling.shtml ,
and referee guidelines at
http://www.nrao.edu/admin/do/refguide/.
Approved programs are scheduled by the VLBA scheduling officers
(Section 24.3), who may be contacted at
``schedsoc@nrao.edu''. Ulvestad (2004) provides a short guide to using
the VLBA, aimed specifically at inexperienced users but also useful to
fill in knowledge gaps for more experienced users.
- The High Sensitivity Array (HSA).
The HSA comprises the VLBA in combination with the VLA2,
the GBT, Effelsberg, and/or Arecibo3.
Observing time of up to 100 hours per trimester has been reserved for
these observations; this opportunity, including the specification of the
HSA in the proposal, is described at
http://www.nrao.edu/HSA/ . Stations from this set also may be
requested individually, though priority will be given to proposals for
the High Sensitivity Array. All deadlines and procedures are the same
as for the VLBA alone.
In this context, users should be aware that Arecibo only operates at
frequencies up to 10 GHz, and can view sources only within about
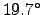 of its zenith; see http://www.naic.edu for further
information about Arecibo's properties.
of its zenith; see http://www.naic.edu for further
information about Arecibo's properties.
- The European VLBI Network (EVN) and
Global cm VLBI. The EVN consists of a VLBI network of stations
operated by an international consortium of institutes (Schilizzi 1995).
The EVN home page at http://www.evlbi.org provides access to the
EVN User Guide. That guide includes the EVN Status Table,
giving details of current observing capabilities of all EVN stations;
and the EVN Call for Proposals, describing how to apply for observing
time on the EVN. The EVN provides proposal, review, and
scheduling mechanisms for such programs, and conducts regular sessions
of 2-3 weeks, 3-4 times per year, to carry out these observations.
EVN proposal deadlines are February 1, June 1, and October 1, with no
allowance made for weekends. EVN session dates, and the wavelengths
to be observed, are given in regular Calls for Proposals, and also
appear in the NRAO Newsletter at
http://www.nrao.edu/news/newsletters/ .
Proposals requesting the EVN in combination with two or more VLBA or
non-EVN VLBA affiliates (identified in Item 5 below) are classified as
``Global cm VLBI'', and must be submitted to both the EVN and the
VLBA. Such observations will be carried out during EVN sessions.
- The Global 3 mm Array. This array
consists of the VLBA stations outfitted at 3 mm, together with
Effelsberg, Pico Veleta, Plateau de Bure, Onsala, and Metsähovi.
The European part of the 3 mm Array is coordinated by the
Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie. For more details and to
submit a proposal, see
http://www.mpifr-bonn.mpg.de/div/vlbi/globalmm/ .
- VLBA affiliates include the VLA,
the GBT, Arecibo, Effelsberg, and the Deep Space Network. A VLBA
proposal requesting such affiliates is handled as described in Item 1
above, except for Global cm VLBI proposals, which are defined and
handled as described in Item 3.
In particular, about 20 days of time per year, outside of regular EVN
sessions, has been reserved for joint VLBI programs involving the VLBA
and Effelsberg; proposals for such joint time are submitted to both the
NRAO and to the EVN scheduler.
The NRAO SCHED program (Walker 2010) can be used to determine the
Greenwich Sidereal Time range during which the VLBI target sources are
visible at various stations. This program can also be used to evaluate
the 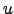 -
-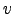 plane coverage and synthesized beams provided by the selected
array.
plane coverage and synthesized beams provided by the selected
array.
A source position service is available through NRAO to obtain accurate
positions for use in correlation (Walker 1999a). This should be requested simultaneously with the proposal, if not earlier. Requirements for source
position accuracy in correlation are discussed by Ulvestad (2004).



Next: 17.2 Submitting a Proposal
Up: 17 VLBA/HSA/EVN/GLOBAL PROPOSALS
Previous: 17 VLBA/HSA/EVN/GLOBAL PROPOSALS
Contents
Stephan Witz
2010-09-21
![]() of its zenith; see http://www.naic.edu for further
information about Arecibo's properties.
of its zenith; see http://www.naic.edu for further
information about Arecibo's properties.